AWS Certified AI Practitioner(1) - IT & AWS Basics
📚 IT & AWS Basics Summary
1. Basic IT Terms
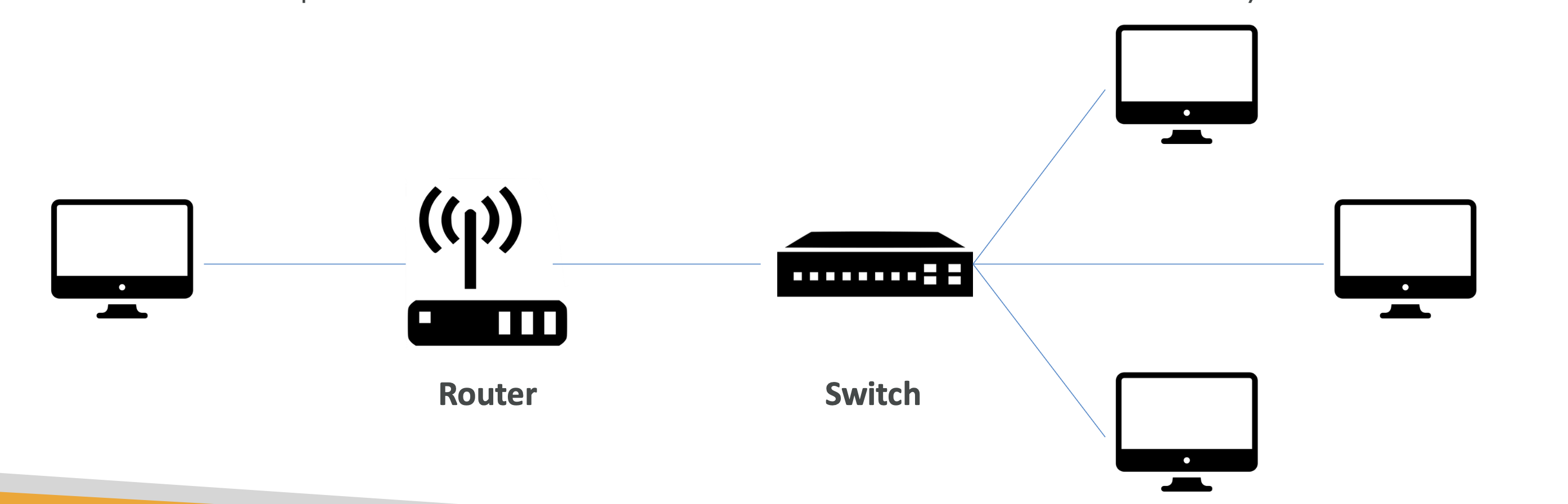
- Network: A connection of cables, routers, and servers.
- Router: A device that decides where to send data packets over the internet.
- Switch: Sends a packet to the correct server or client within the network.
2. Five Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand self service – Instantly get resources without human help.
- Broad network access – Access resources from different devices via the internet.
- Multi-tenancy & Resource pooling – Multiple users share the same resources securely.
- Rapid elasticity & Scalability – Quickly scale up or down when needed.
- Measured service – Pay only for the resources you use.
3. Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
- No need to buy hardware; pay only for what you use.
- Lower costs through large-scale efficiency.
- Scale based on real usage.
- Faster development and deployment.
- No need to run and maintain your own data center.
- Go global within minutes.
4. Problems Solved by the Cloud
- Flexibility: Change resource types anytime.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go model.
- Scalability: Handle higher loads by adding or upgrading hardware.
- Elasticity: Scale in and out when needed.
- High availability & Fault tolerance: Spread across multiple data centers.
- Agility: Develop and launch quickly.
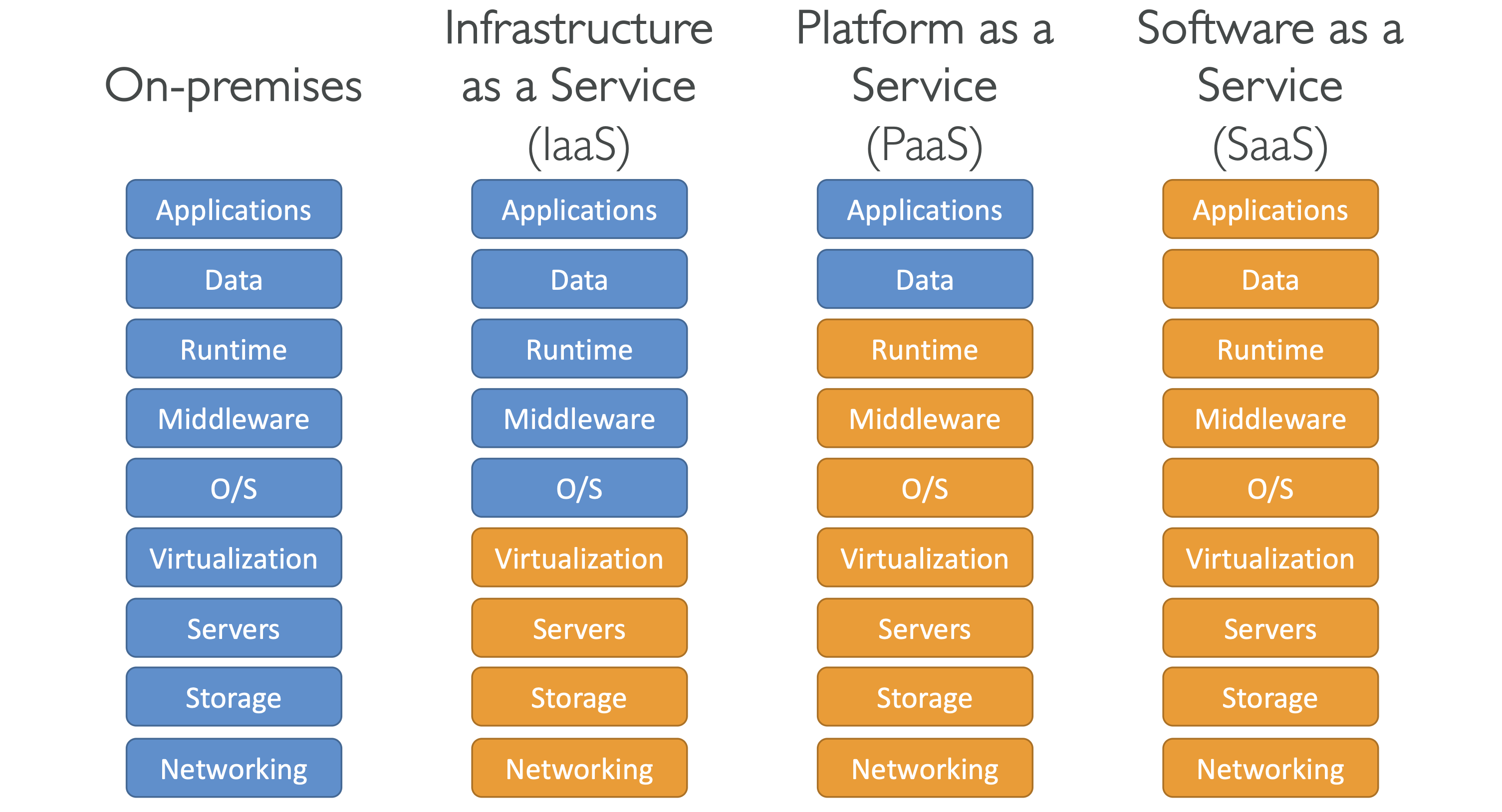
5. Cloud Service Types – Examples
- IaaS: AWS EC2, GCP, Azure.
- PaaS: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku.
- SaaS: Gmail, Dropbox, Zoom.
6. AWS Pricing Basics
- Compute: Pay for the time you use computing resources.
- Storage: Pay for the data stored in the cloud.
- Data Transfer: Pay for data going out of the cloud (incoming is free).
7. AWS Regions
- A region is a cluster of data centers around the world.
- Choosing a region depends on:
- Legal & compliance requirements.
- Distance to customers (lower latency).
- Services available in the region.
- Pricing differences.
8. AWS Availability Zones (AZ)
- Each region has 3–6 independent data centers.
- Redundant power, networking, and connectivity.
- Separated to avoid disasters and connected with high-speed, low-latency links.
9. AWS Edge Locations (Points of Presence)
- 400+ locations in over 90 cities across 40+ countries.
- Deliver content to users with lower latency.
10. AWS Service Scope
- Global services: IAM, Route 53, CloudFront, WAF.
- Region-specific services: EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, Rekognition.
All articles on this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless otherwise stated.
